 The logistics industry is vital to global trade and is responsible for moving goods efficiently across borders. However, it contributes significantly to environmental degradation, particularly through emissions, resource depletion, and waste. As the world shifts towards sustainability, the logistics sector is being called upon to adopt eco-friendly practices. This article explores various eco solutions currently shaping the future of the logistics industry.
The logistics industry is vital to global trade and is responsible for moving goods efficiently across borders. However, it contributes significantly to environmental degradation, particularly through emissions, resource depletion, and waste. As the world shifts towards sustainability, the logistics sector is being called upon to adopt eco-friendly practices. This article explores various eco solutions currently shaping the future of the logistics industry.
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Alternative Fuels
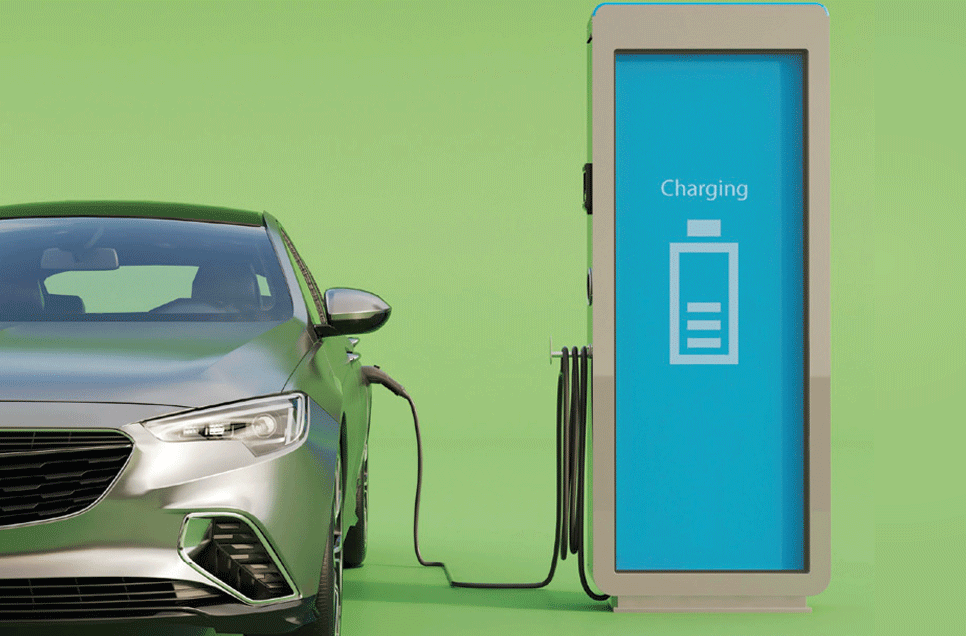 The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) in logistics is a key development aimed at reducing carbon emissions. These vehicles are powered by renewable energy sources like solar and wind, producing zero tailpipe emissions. Major logistics companies like UPS, FedEx, and DHL have already invested in electric delivery vans and trucks.Apart from EVs, the industry is exploring alternative fuels such as:
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) in logistics is a key development aimed at reducing carbon emissions. These vehicles are powered by renewable energy sources like solar and wind, producing zero tailpipe emissions. Major logistics companies like UPS, FedEx, and DHL have already invested in electric delivery vans and trucks.Apart from EVs, the industry is exploring alternative fuels such as:
• Hydrogen fuel cells: Promising clean energy for long-haul freight, hydrogen-powered trucks are expected to significantly reduce the carbon footprint.
• Biofuels: Derived from organic matter, biofuels are an eco-friendly alternative to traditional diesel, offering lower greenhouse gas emissions.
• Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) is a cleaner-burning fuel that emits fewer pollutants than gasoline or diesel.
2. Green Warehousing
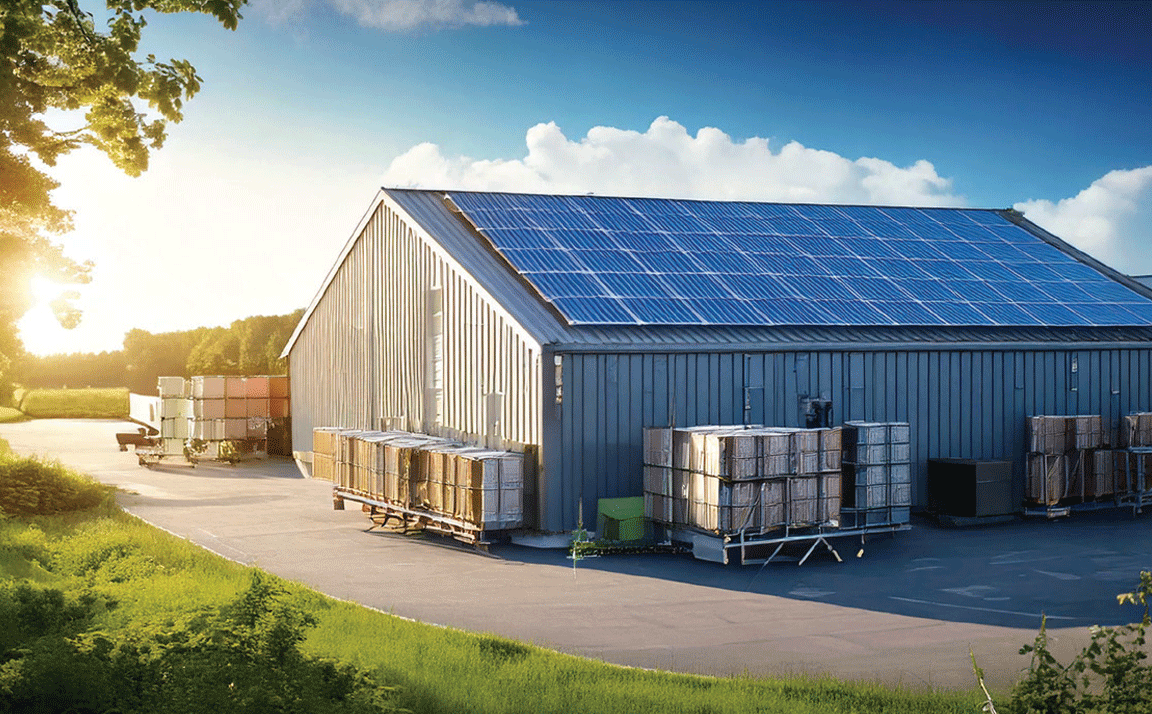
 Warehouses, being energy-intensive facilities, offer multiple opportunities for sustainability. Green warehousing focuses on reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and utilizing renewable energy sources. Key solutions include:
Warehouses, being energy-intensive facilities, offer multiple opportunities for sustainability. Green warehousing focuses on reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and utilizing renewable energy sources. Key solutions include:
• Energy-efficient lighting: Replacing traditional lighting systems with LED lights can reduce energy consumption by up to 75%. Motion sensors and natural lighting designs can further reduce energy use.
• Solar-powered warehouses: Installing solar panels on warehouse roofs allows logistics companies to harness renewable energy, reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
• Eco-friendly building materials: Warehouses can be constructed or retrofitted with materials that have lower environmental impacts, such as recycled steel or sustainable concrete.
3. Sustainable Packaging
Packaging waste is a significant issue in logistics, especially with the rise of e-commerce. To counteract this, many companies are adopting sustainable packaging practices. These include:
• Biodegradable materials: Using packaging made from plant-based materials, such as cornstarch, reduces plastic waste and the environmental impact of landfills.
• Recyclable materials: Companies increasingly use recyclable paper, cardboard, and plastic for packaging.
• Right-sizing: Using the right-sized packaging for products reduces excess material use, optimizes space in transportation, and lowers fuel consumption.
• Reusable packaging: Logistics firms are developing reusable containers and pallets for transporting goods, minimizing the waste associated with single-use packaging.
4. Efficient Transportation Networks
Improving transportation efficiency can drastically cut emissions. Some eco-friendly strategies include:
• Route optimization: Advanced algorithms can help optimize delivery routes to minimize fuel consumption and travel time. By reducing travel distances, companies lower their carbon emissions and operational costs.
• Freight consolidation: Combining smaller shipments into a single truckload reduces the number of trips, cutting down on fuel use and emissions.
• Intermodal transportation: Utilizing multiple modes of transport (e.g., combining rail, sea, and road) for long-distance freight can be more fuel-efficient and eco-friendly. Rail and sea transport typically emit less CO2 than road transport, making them more sustainable alternatives for bulk shipments.
5. Eco-friendly Shipping Practices
 Sea freight is one of the most environmentally efficient means of transportation, but it still contributes to pollution. The following eco-solutions are helping to reduce the environmental impact of shipping:
Sea freight is one of the most environmentally efficient means of transportation, but it still contributes to pollution. The following eco-solutions are helping to reduce the environmental impact of shipping:
• Slow steaming: Ships traveling at reduced speeds burn less fuel, lowering their CO2 emissions. While this may extend delivery times, it significantly cuts down on environmental harm.
• Ballast water management: Ships often carry ballast water to maintain stability, but releasing it can introduce invasive species into ecosystems. Modern ships have ballast water treatment systems that purify the water before discharge.
• Cleaner ship fuels: The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has introduced new regulations to reduce the sulfur content of ship fuels, leading to cleaner emissions. Some shipping companies also invest in Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) and biofuels as green alternatives.
6. Circular Supply Chain Models
A circular supply chain focuses on minimizing waste and reusing materials. The circular model promotes resource recovery and product lifecycle extension instead of a traditional linear supply chain (make, use, dispose). In logistics, this can involve:
• Reverse logistics: Returning used products to suppliers for recycling, refurbishment, or remanufacturing helps to reduce waste and raw material consumption.
• Sharing economy: Logistics companies can share assets such as warehouses and trucks with other businesses to optimize resource use and minimize environmental impact.
7. Sustainable IT Solutions
 Technology plays a crucial role in driving sustainability in logistics. From cloud computing to blockchain, IT solutions are helping logistics firms track, optimize, and reduce their environmental footprint.
Technology plays a crucial role in driving sustainability in logistics. From cloud computing to blockchain, IT solutions are helping logistics firms track, optimize, and reduce their environmental footprint.
• Smart fleet management systems: IoT (Internet of Things) devices can monitor vehicle performance, fuel consumption, and driver behavior in real time, providing actionable insights for reducing emissions.
• Blockchain for transparency: Blockchain technology offers transparency in the supply chain, helping companies track and verify the environmental impact of their logistics processes.
8. Carbon Offsetting Initiatives
Even with the adoption of eco solutions, some emissions are inevitable. Carbon offsetting allows companies to invest in environmental projects that reduce or capture carbon, such as reforestation or renewable energy projects, to compensate for their emissions.
Conclusion
The logistics industry is undergoing a transformative shift towards sustainability. Companies can reduce their environmental impact by adopting electric vehicles, optimizing transportation routes, embracing green warehousing, and implementing sustainable packaging. As governments and consumers demand more eco-conscious practices, the logistics sector has the potential to play a crucial role in creating a more sustainable future. Implementing these eco-solutions benefits the environment and offers cost savings, operational efficiencies, and a competitive edge for businesses prepared to lead the charge in green logistics.